Git and github¶
Introduction to git¶
All data and code is managed using git as version control system in combination with GitHub. A good introduction about the advantages of Git and GitHub in bioinformatics is Perez-Riverol2019.
Version control is a system that records changes to a file or set of files over time so that you can recall specific versions later. It allows multiple people to work cooperatively on a project. For an introduction read getting started - about version control and getting started - what is git.
Multiple people can work together on a single project by having local copies of a repository which are synchronized with the remote repository.
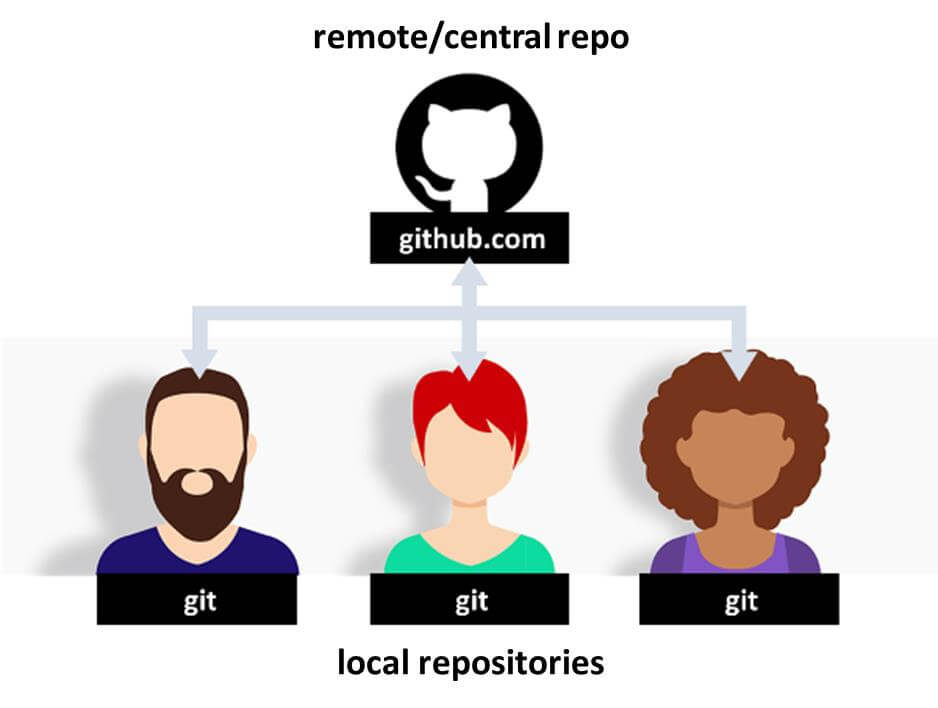
Various online online resources provide an interactive introduction to the concepts of git, see for instance https://try.github.io/. We recommend to do the following short online course giving an overview of the core git commands such as branch, add, commit, merge.
Online course: https://learngitbranching.js.org/.
Most important git commands¶
The following cheat sheet provides an overview over the most important git commands: github-git-cheat-sheet.
Initial setup¶
After git installation you should first setup your environment.
Set the name you want attached to your commit transactions:
git config --global user.name "[name]"
Set the email you want attached to your commit transactions:
git config --global user.email "[email address]"
Enable helpful colorization of command line output:
git config --global color.ui auto
Working with a repository¶
In this section we provide a basic overview of the main workflow and commands used with git.
The normal workflow consists of getting a local copy of the repository (clone). After modifying files locally this are added to git (add) and the changes are uploaded again (commit). By pulling the latest changes (pull) an existing copy can be updated. Command such as status, diff and log provide information about the current status and the history of the repository.
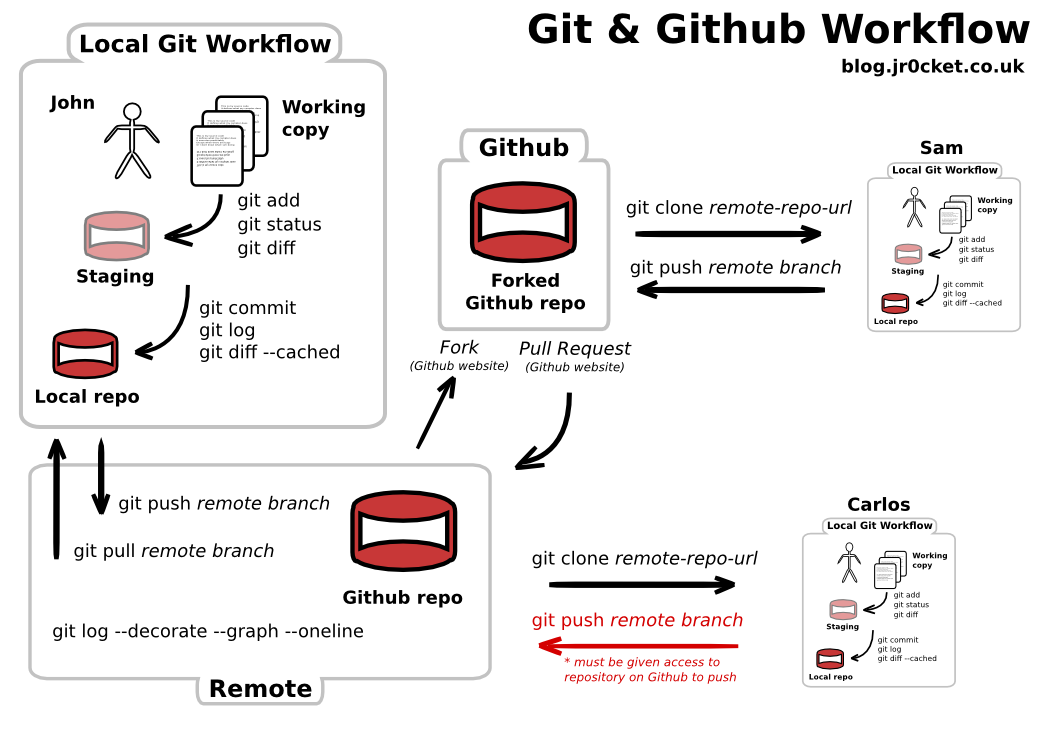
To work with a project first you have to clone the repository, i.e., getting a local copy.
Clone (download) a repository that already exists on GitHub, including all of the files, branches, and commits:
git clone [url]
Next make sure you work on the right branch, i.e., you have to switch the branch. Switch to the specified branch and updates the working directory:
git checkout [branch-name]
After making changes to files, these have to be added and commited. Snapshot the file in preparation for versioning.:
git add [file]
Record file snapshots permanently in version history:
git commit -m "[descriptive message]"
GitHub¶
We use GitHub as a platform to work with git. The next step is to complete the free online course on GitHub (after you created an account on https://github.com). The course is available from https://lab.github.com/githubtraining/introduction-to-github.
You will learn
What is GitHub?
How does one use GitHub?
What are issues and pull requests?
How do you create a branch and a commit?
How do you use GitHub Pages?
And when you’re done you’ll be able to:
Communicate in issues
Manage notifications
Create branches
Make commits
Introduce changes with pull requests
Deploy a web page to GitHub pages
After following the basic tutorials you are ready to work on a real project.
Resources¶
git book - Getting started - About version control, https://git-scm.com/book/en/v2/Getting-Started-About-Version-Control
git book - Getting started - What is git?, https://git-scm.com/book/en/v2/Getting-Started-What-is-Git%3F
resources to learn git, https://try.github.io/
online course git; https://learngitbranching.js.org/
github course, https://lab.github.com/githubtraining/introduction-to-github
Perez-Riverol Y, Gatto L, Wang R, Sachsenberg T, Uszkoreit J, Leprevost Fda V, Fufezan C, Ternent T, Eglen SJ, Katz DS, Pollard TJ, Konovalov A, Flight RM, Blin K, Vizcaíno JA. Ten Simple Rules for Taking Advantage of Git and GitHub. PLoS Comput Biol. 2016 Jul 14;12(7):e1004947. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1004947. Erratum in: PLoS Comput Biol. 2019 Jun 14;15(6):e1007142. PMID: 27415786; PMCID: PMC4945047.
PDF